Addressing and mitigating hazards is one of Montana's main priorities due to legal and ethical responsibilities, the increasing costs of response and recovery, and many events being predictable and repetitive.
Hover over each photo to learn more about each hazard. Some photos depict actual hazard events that occured in Montana.
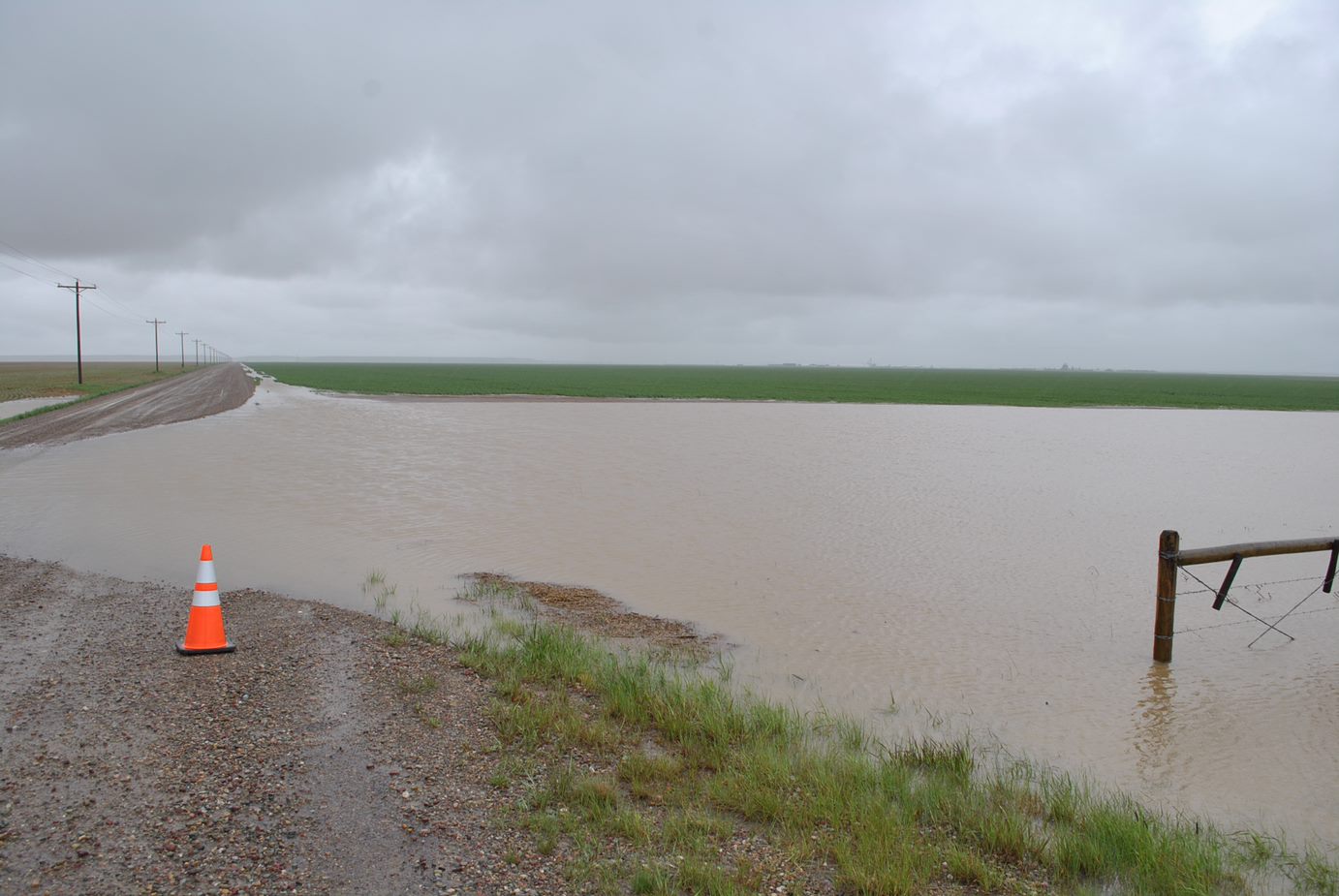

Flooding
Flooding is defined by the rising and overflowing of water onto normally dry land. Flooding can result from an overflow of inland waters or an unusual accumulation or runoff of surface waters from any source.
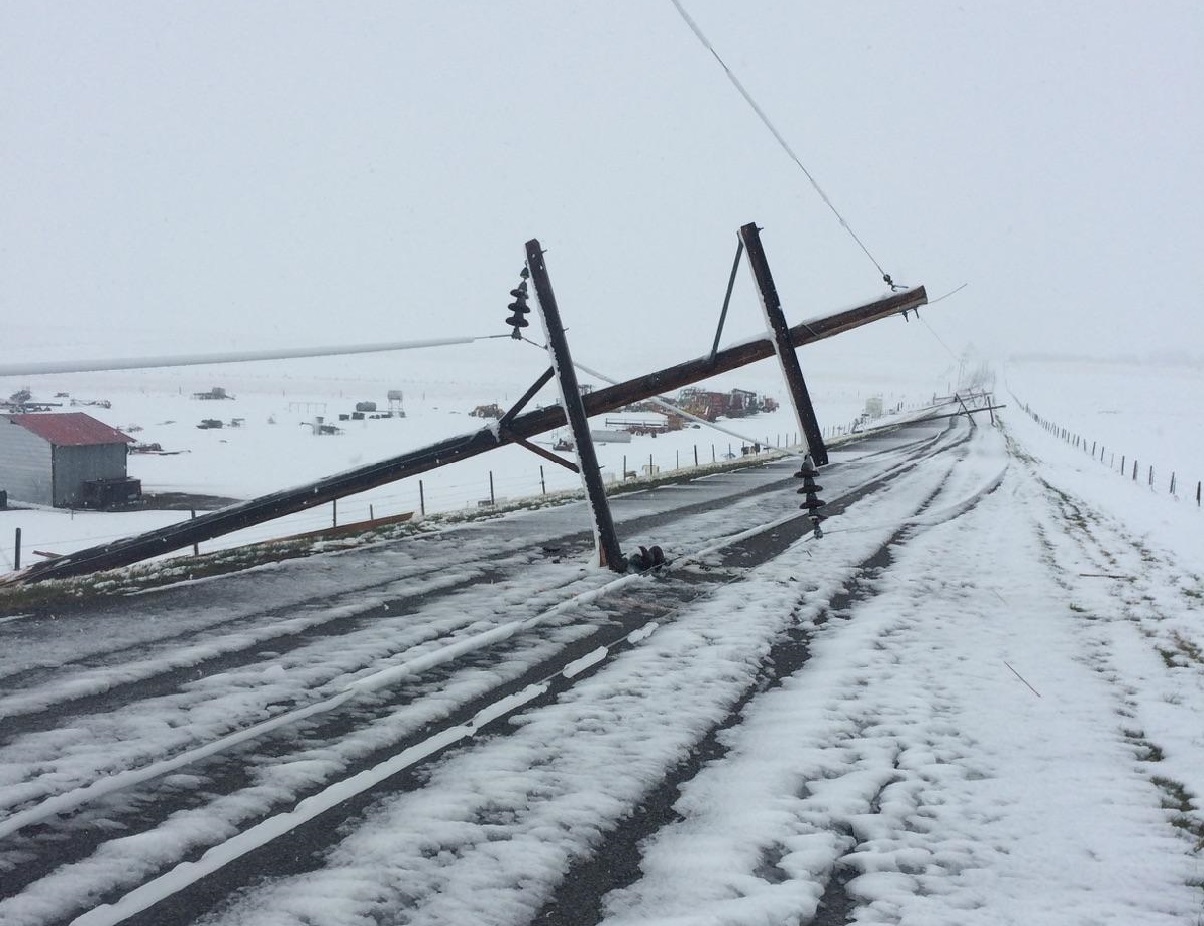

Severe Seasonal Weather
Severe seasonal weather includes both severe summer and winter weather hazards. Severe summer weather includes thunderstorms, hailstorms, lightning and extreme heat. Severe winter weather includes heavy snow, blizzards, ice storms and extreme cold. Severe seasonal weather can result in dangerous conditions including blocked roads and sidewalks, downed trees and powerlines and exposure to severe conditions.
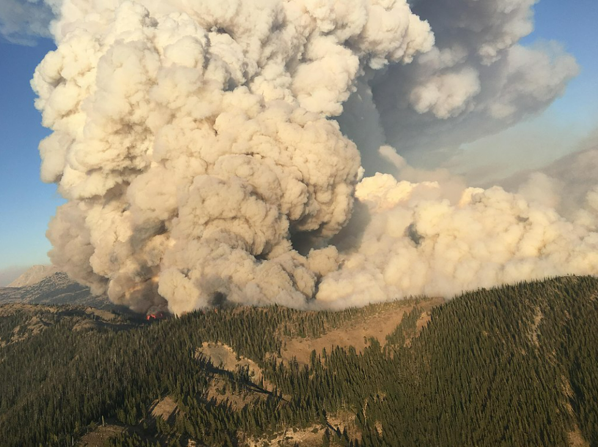

Wildfire
A wildfire is an uncontained fire that spreads through the environment. Wildfires have the ability to consume large areas, including infrastructure, property, and resources.
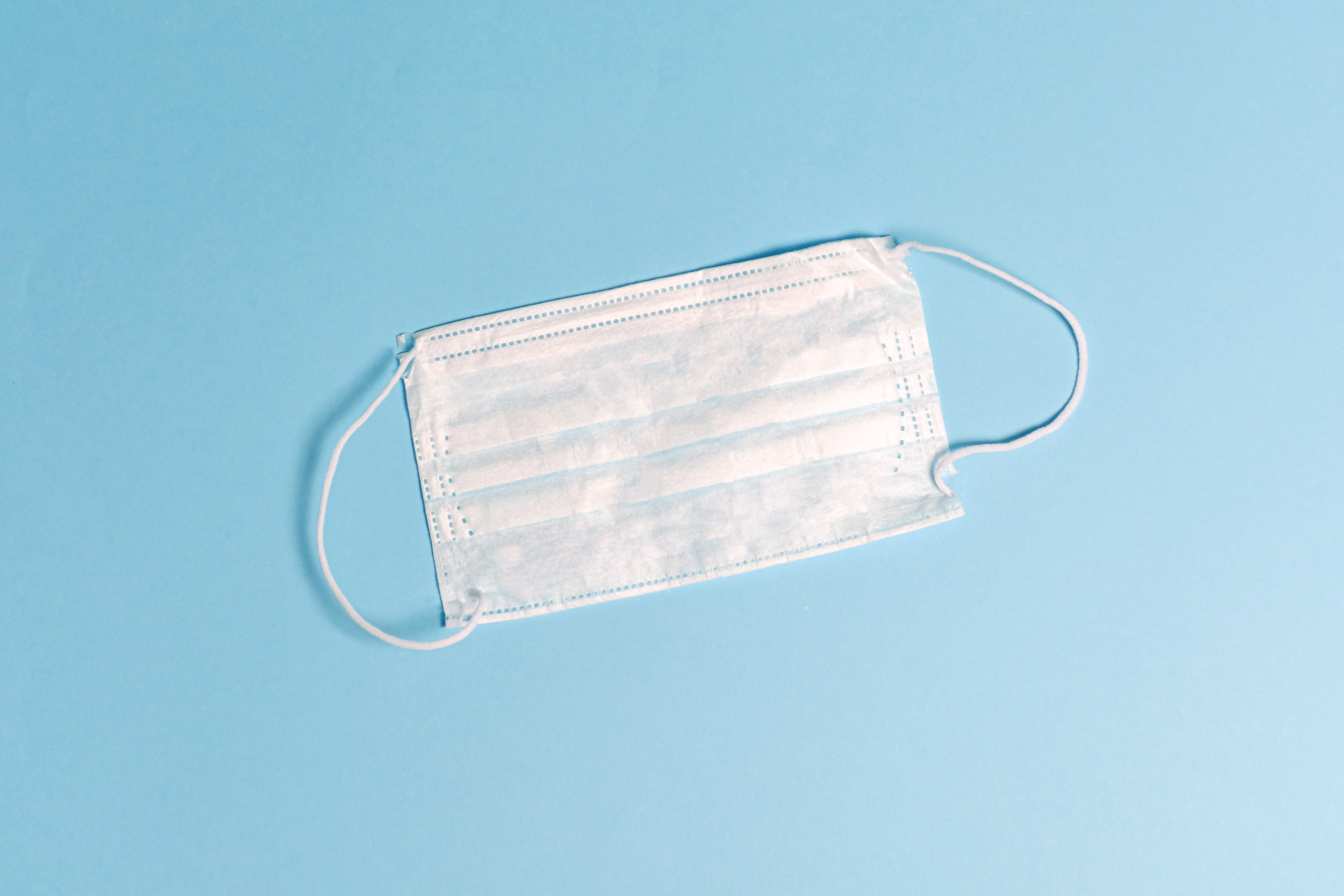

Communicable Disease
Communicable disease is a public health threat that can cause isolation, quarantine, and potential mass casualties. Disease spread and mortality is affected by a variety of factors, including virulence, ease of spread, aggressiveness of the virus and its symptoms, resistance to known antibiotics and environmental factors. Impacts of communicable disease can range from school and business closings to the interruption of basic services.

Cyber-Attack
A cyber threat is any deliberate attack on information technology systems in an attempt to gain illegal access to a computer, or purposely cause damage. Cyber-attacks use malicious code to alter computer operations or data.

Dam Failure
A dam failure is the collapse or breach of a dam that causes downstream flooding. Dam failures may be caused by natural events, manmade events, or a combination. Due to the lack of advance warning, failures resulting from natural events, such as earthquakes or landslides, may be particularly severe. Prolonged rainfall and subsequent flooding is the most common cause of dam failure.

Drought
Drought is a deficiency in precipitation over an extended period. It is a normal, recurrent feature of climate that occurs in virtually all climate zones. However, drought can affect people’s health and safety. It has the potential to impact water supply, agricultural yields, and water-dependent industries. Drought conditions can also increase the likelihood of wind erosion and increase wildfire risk.

Earthquake
An earthquake is a movement or shaking of the ground. Most earthquakes are caused by the release of stresses accumulated as a result of the rupture of rocks along opposing fault planes in the Earth’s outer crust.

Hazardous Materials Incidents
A hazardous material is any item or agent (biological, chemical, physical) which has the potential to cause harm to humans, animals, or the environment, either by itself or through interaction with other factors. A release or spill of bulk hazardous materials could result in fire, explosion, toxic cloud or direct contamination of people and property. The effects may involve a local site or many square miles. Health problems may be immediate, such as corrosive effects on skin and lungs, or be gradual, such as the development of cancer from a carcinogen. Damage to property could range from immediate destruction by explosion to permanent contamination by a persistent hazardous material.

Landslide
Landslides are defined as natural or unnatural massive movements of rock, soil, or earth down slopes. Landslides can have multiple causes - typically those causes include but are not limited to: rainfall, snowmelt, changes in water level, erosion, and disturbance by human activity.

Terrorism and Mass Violence
Terrorism is defined in the United States by the Code of Federal Regulations as: “the unlawful use of force and violence against persons or property to intimidate or coerce a government, the civilian population, or any segment thereof, in furtherance of political or social objectives.” A terror threat is generally more likely to be targeted at a critical or symbolic location.
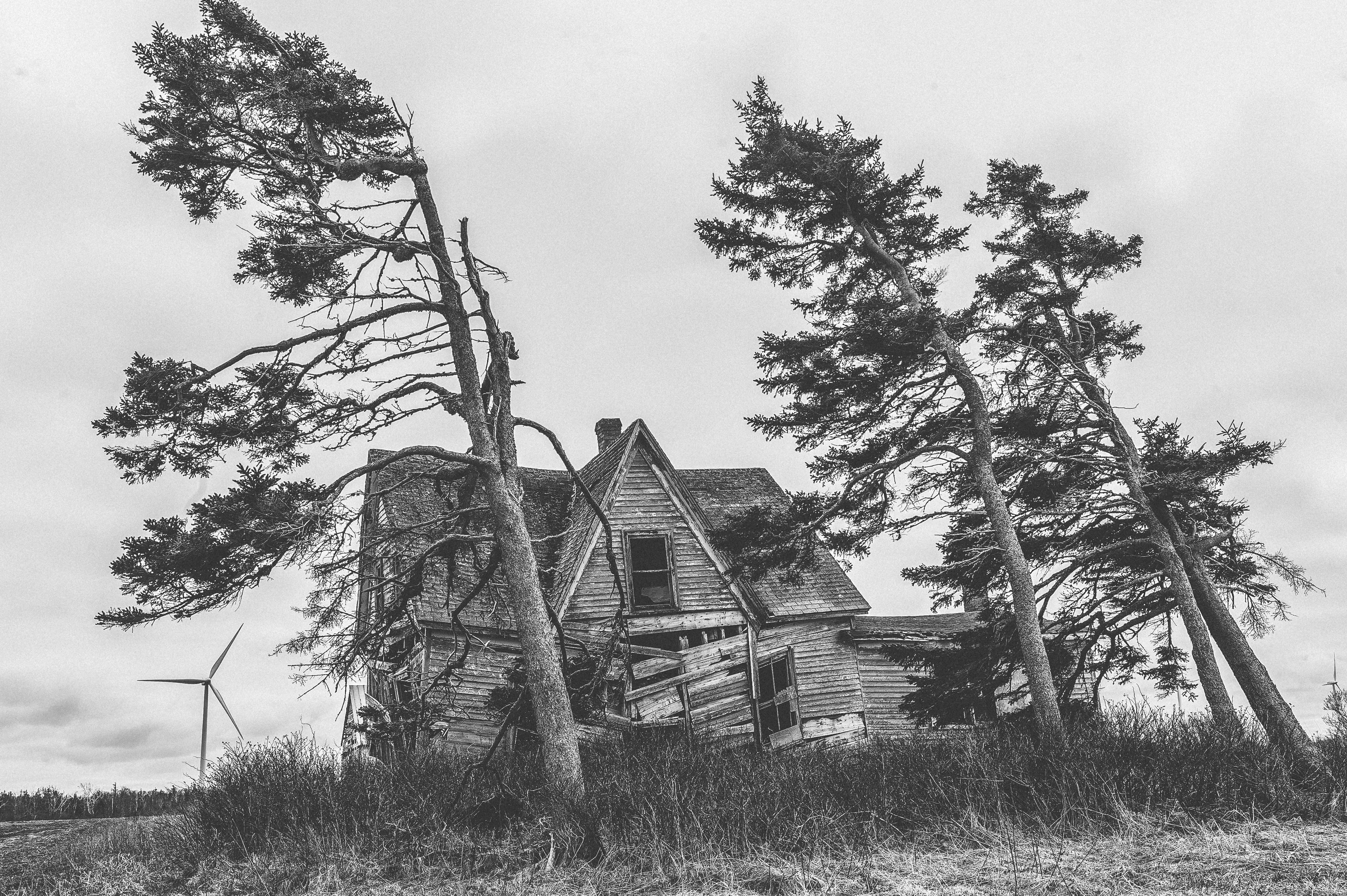

Tornadoes & Windstorms
A tornado appears as a rotating, funnel-shaped cloud that extends from a thunderstorm to the ground with whirling winds that can reach 300 miles per hour. Damage paths can be in excess of one mile wide and 50 miles long.
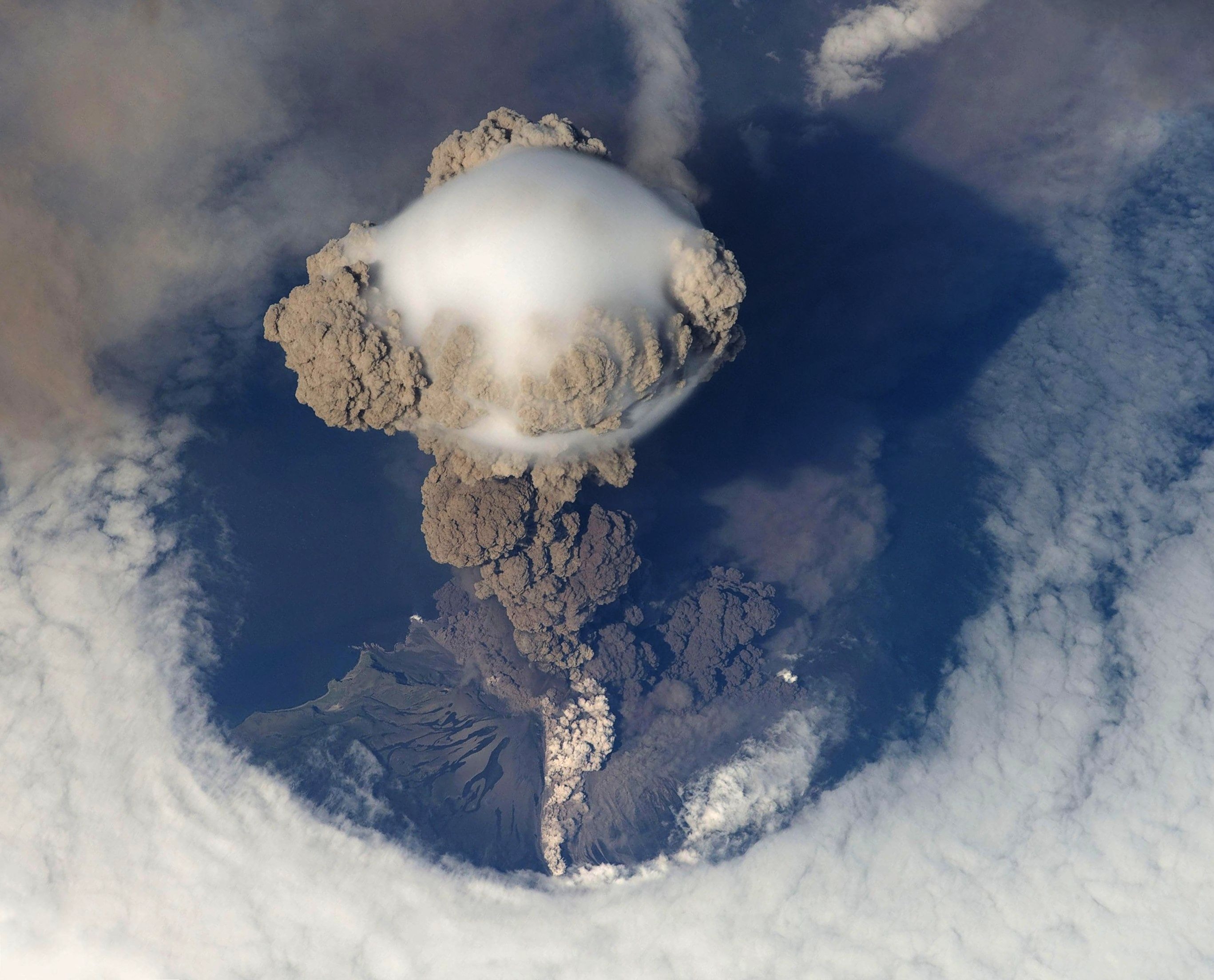

Volcanic Ash
Volcanic ash consists of rocks, minerals, and gasses that are dispersed as a result of volcanic erruptions. Volcanic ash can lead to power outages, health issues, and destruction of buildings under the ash's weight.
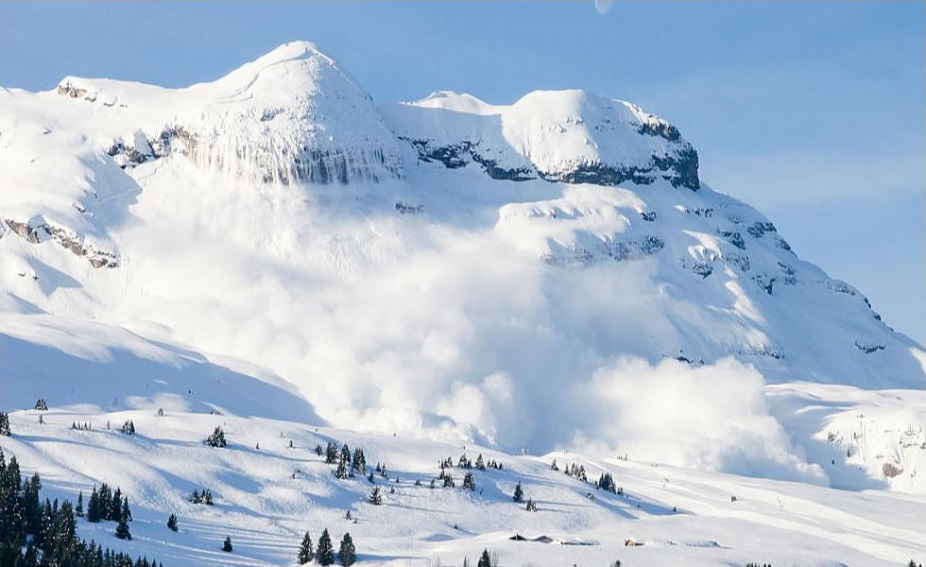

Avalanche
An avalanche is a mass of loosened snow, ice, and/or earth suddenly and swiftly sliding down a mountain. Avalanches are often the result of severe winter weather and pose a risk to recreationists, communication and transportation networks in mountainous regions.